1-877-795-2278 | info@aircraftspruce.ca
Aircraft Spruce Canada
Brantford, ON Canada
Corona, CA | Peachtree City, GA
Chicago, IL | Wasilla, AK
Aircraft Spruce Canada
Brantford, ON Canada
Corona, CA | Peachtree City, GA
Chicago, IL | Wasilla, AK
FREE SHIPPING ON ORDERS OVER $699 (SOME EXCLUSIONS APPLY) | 877-795-2278
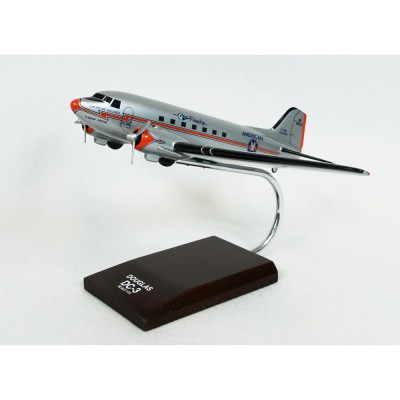
DC-3 American Model
$307.00/Each
Part# 13-10971
MFR Model# KDC3AAT
MFR Model# KDC3AAT
Overview
|
The Douglas DC-3, first flew on December 17, 1935, is a fixed-wing, propeller-driven aircraft whose speed and range revolutionized air transport in the 1930s and 1940s. Many names and numbers were assigned to the DC-3. England labeled it the ""Dakota"" or ""Dak."" American pilots, during World War II, called it the “Skytrain”, ""Skytrooper”, ""Doug,"" or ""Gooney Bird."" The U.S. military’s official titles were C-47, C-53, C-117, and R4D. The airlines called it ""The Three."" Of all the names the affectionate title ""Gooney Bird"" lingers on. The D-13 had a lasting impact on the airline industry and World War II. It was generally regarded as one of the most significant transport aircraft ever made. The D-3 was intended at the height of the depression and in the infancy of the Airline Industry by Douglas Aircraft Company. It carried 34 passengers in more comfort than previous airliners. D-3, a much faster, more efficient and safer airplane, was purchased by many airlines all around the world. Production was diverted during World War II to the C-47 military version and many civilian airliners were converted to the military requirements for use during the war. After the war, most of the DC-3s and C-47s were returned to civilian and commercial use and others were sold to allied air forces around the world. The DC-3 once again was carrying paid passengers and was still in service carrying passengers in the 1970s with a few airlines. Today the DC-3s are relegated to aircraft museums, graveyards and occasionally a charter outfit still carrying cargo in them. |
Q&A
Please note, Aircraft Spruce Canada's personnel are not certified aircraft mechanics and can only provide general support and ideas, which should not be relied upon or implemented in lieu of consulting an A&P or other qualified technician. Aircraft Spruce Canada assumes no responsibility or liability for any issue or problem which may arise from any repair, modification or other work done from this knowledge base. Any product eligibility information provided here is based on general application guides and we recommend always referring to your specific aircraft parts manual, the parts manufacturer or consulting with a qualified mechanic.

 Aircraft Spruce Canada
Aircraft Spruce Canada